
Mr. Vivek Chougule
Managing Director of Eka Global India
IMPORTANCE OF BARRIER CONTAINERS & LID FILMS
Today’s consumers are greeted with innovative packaging options in the market. Significant consideration and science goes into selecting the correct packaging materials. Packaging is an essential medium for protecting food quality, minimising food wastage and reducing preservatives used in food. Packaging protects against damage or contamination by micro-organisms, air, moisture and toxins.
With an increasingly global food retailing customer base, food packaging must meet longer shelf-life requirements and adherence to international food safety/quality standards. Food-purchasing decisions are based on taste and appearance as well as shelf life and convenience, making excellent barrier quality to maintain product freshness vital in food packaging - not only to extend shelf life, but also to improve consumer experience. Due to its increased shelf-life the brand owners can expand their market. They can establish their brand globally and increase their brand value. The distribution network can be widened to General Trade, Modern Trade, E-commerce, etc. Even if barrier packaging costs more upfront, it protects the bottom line and grows the top line.
Barrier packaging is vital for all three Pillars of Shelf Life, namely 1. Microbiological Safety, 2. Appealing Sensory, 3. Protecting Nutrition. Food manufacturers must ensure that their food products are kept safe and free of contamination at all stages in their journey from manufacturing facility to retail shelf. The temperature and humidity conditions to which a product is likely to be exposed in the supply chain are vital in calculating the required barrier. Thus, it is essential to specify these and check that the data being quoted are applicable to the conditions expected. Transparency or clarity can be extremely important in marketing. On the other hand, food can be adversely a ected by prolonged exposure to light in transparent packaging.
KEY FUNCTIONS OF FOOD PACKAGING
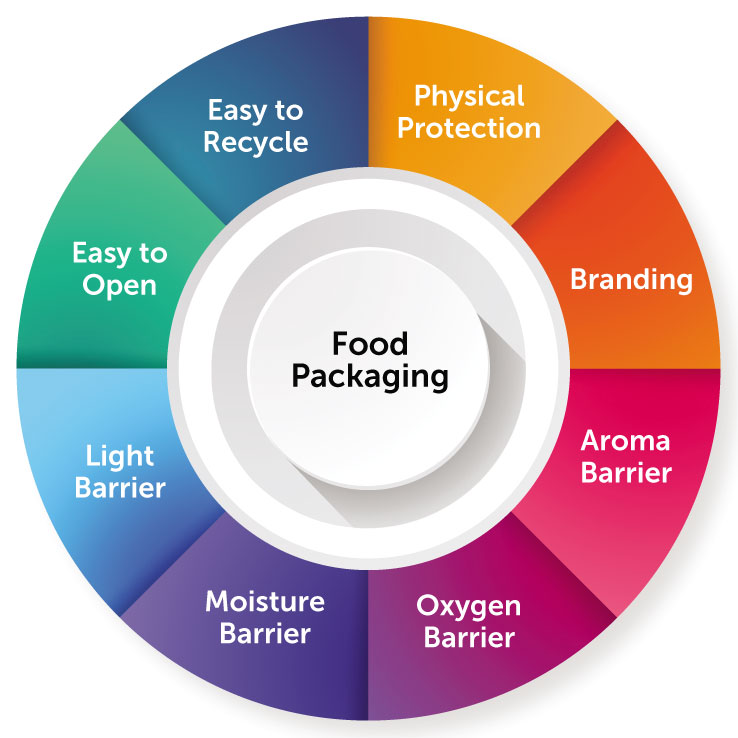
Food packaging uses a variety of di erent materials to protect food. The types of material used in food packaging will depend on the type of food product, product weight to package surface area ratio, type of processing method, target shelf life, and supply chain conditions. The possibilities are truly endless when it comes to designs. Specific packaging designs can be developed as per the brand’s requirements, which make the products more noticeable to consumers and aid in marketing.
An important requirement in selecting food packaging systems is the barrier properties of the packaging material. Barrier properties include permeability of gases (such as O2, CO2, and N2), water vapour, aroma compounds and light. These are vital factors for maintaining the microbial safety and quality of packaged foods. In general, the permeability of plastic packaging depends on its characteristics (such as crystallinity, molecular orientation, chain sti ness, free volume, cohesive energy density, etc.), permeate properties (such as molecule size and nature) and external conditions (such as temperature, moisture etc.). Food packaging provides varying degrees of protection, depending largely on the nature of the polymers and structures made by the combination of polymers. Improvements in the barrier properties can be obtained by combination of appropriate polymers and polymers processing technologies. For example, biaxial orientation results in increased toughness, increased sti ness, enhanced clarity, and enhanced barrier properties. However it is di cult to obtain all the desirable barrier properties from a single polymeric material. Thus various techniques are used to create a composite structure. Some of the most popular techniques are lamination, co-extrusion, coating, and combination of these to meet the varied barrier requirements of food packaging.
For example, PP has a good moisture barrier property but poor oxygen resistant property. On the other hand Ethylene-vinyl alcohol (EVOH) has a good oxygen barrier property but poor moisture barrier. These polymers can be combined along with others to provide optimum barrier properties for range of adverse elements. Barrier packaging works hard to keep harmful elements like oxygen, water, water vapor, aromas, light, grease, oils, and more away from your goods. This makes barrier containers a great option for products that normally have short shelf life. Along with the barrier containers, high barrier lid films with Easy Peel performance are critical in achieving desired results.
Typical Barrier Container Packaging Structures & Applications
| Barrier Category | Typical Structures of Containers & Lid Film | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
Ultra High |
Multi layer structures with Oxygen Scavengers, Foil/SiOx & AlOx Coated Barrier Films |
Long Shelf Life: RTE, Baby Food, Pet Food, Retort Products |
High |
Multi layer structures with multiple barrier layers, SiOx & AlOx Coated Barrier Films |
Extended Shelf Life: Ethnic Sweets, Bakery, Dry Fruits etc MAP Products, Chilled Meals |
Medium |
Multi layer structures with single barrier layer, Polyamide (Nylon) based Barrier Films |
Extended Shelf Life at chilled storage: Paneer, Meats |
Low |
Single layer structures without barrier layer and Non Barrier Films |
Short Shelf Life at chilled or Long Shelf Life at frozen storage: Dahi, Ice-cream Frozen Foods |
ADVANCES IN BARRIER PACKAGING
Material developments and new packaging processes are allowing food to be kept fresh much longer without altering taste or aroma. While traditional barrier materials extend product shelf life by impeding O2 migration into a package, in built O2 scavengers go one step further "capturing" O2 present within a sealed package to ensure it does not react with the food product. By combining active and barrier packaging, processors can increase shelf life, protect flavor profiles and maintain food's appearance without adding preservatives. Antimicrobials as a coating or compounded into the plastic are helping address outbreaks of foodborne illnesses.
Combinations of barrier technology and processing advances such as MAP, Retort and MATS are resulting in unique food-product advances. Nanotechnology is also being used to enhance packaging barrier properties. New nano-based food packaging materials with improved mechanical, barrier and antimicrobial properties, and nano-sensors for traceability and monitoring food condition during transport/storage are key development areas for nanotechnology in food packaging. Barrier technology continues to improve and so-called ‘active and intelligent’ packaging is becoming a reality. Active packaging can been seen as a means of maintaining the optimum (desired barrier) conditions to which a food is exposed, while intelligent packaging detects the status of foods (e.g. quality, maturity) inside the package.
Packaging waste is a growing environmental concern, and consumers are seeking more sustainable packaging choices. Range of recyclable materials made from Post Consumer Recycle (PCR) and Bio Based sourcing are becoming available.
Food
- Snacks & Namkeen Packaging Machine in Bangladesh
- Ready-to-Eat Food Packaging Machine in Bangladesh
- Grains & Seeds Packaging Machine in Bangladesh
- Milk & liquids Packaging Machine in Bangladesh
- Powder Packaging Machine in Bangladesh
- Spice Packaging Machine in Bangladesh
- Coffee Packaging Machine in Bangladesh
- Sugar Packaging Machine in Bangladesh
- Oil Packaging Machine in Bangladesh
- Salt Packaging Machine in Bangladesh
- Tea Packaging Machine in Bangladesh
Non Food
- Agrochemicals in Bangladesh
- Fertilizer in Bangladesh
- Adhesives in Bangladesh
- Lube oil, Varnishes, Coolants in Bangladesh
- Paint powder in Bangladesh
- Hardware in Bangladesh
- Pet foods in Bangladesh
- Cement & wall putty in Bangladesh
- Dyes and pigments in Bangladesh
- Foundry, Flux and Inoculants in Bangladesh


